
Imagine being in a huge library with millions of books, yet no librarian to help you find the book you want to read, and no card catalogue to help you search for that book. This is precisely what the digital world without automatic Text Classification looks like.
In a world of automation, AI, and data-driven decisions, machines need to read, comprehend, and organize language at a scale. That’s where the text classification works as a silent engine powering modern AI system, from spam filters to intelligent agents. Let’s get insights into the text classification covering each relevant concept.
What is Text Classification?
Text Classification, which is also called Text Categorization (TC), is one of the foundational tasks in Natural Language Processing (NLP) and text mining. It is the process of categorizing texts into various categories or classes, such as documents, emails, social media posts, or web pages.
Fundamentally, TC is used to organize and structure the unstructured text in a meaningful way. For that, rather than involving people to manually read and categorize information, Text classification techniques in machine intelligence are used to detect patterns, topics, sentiment, and intent in text.
Benefits of Text Classification Over Manual Methods
Were you aware that, according to Forbes, the job listings referenced AI skills have increased by 2.8 percent after mid 2025, with a much higher concentration in high-paying jobs? Therefore, exploring the benefits of automatic text classification helps build AI skills in 2026.
Key Benefits of Text Classification:
It's no longer feasible to manually classify text in an era where petabytes of text are generated each day. That’s why automatic text classification is prioritized in today’s modern ecosystems.
Core Approaches Used in Text Classification
Machine learning and deep learning paradigms are employed in text classification systems, which are well-suited in relation to data availability and problem complexity.
1. Supervised Learning
In supervised models, algorithms are trained using labeled datasets where each document is already assigned as a category.
Common Machine Learning Algorithms Used:
2. Unsupervised Learning
When it comes to unlabeled data, unsupervised learning methods discover latent patterns within the given text.
Common Unsupervised Learning Techniques Used:
These techniques cluster documents by semantic affinity, revealing hidden topics without predefined labels.
To understand the depth of unsupervised learning, explore the latest insight on Autoencoders Simplified - The Core of Unsupervised Learning.
Types of Text Classification Tasks
Text classification tasks are different depending on the text categories assigned.
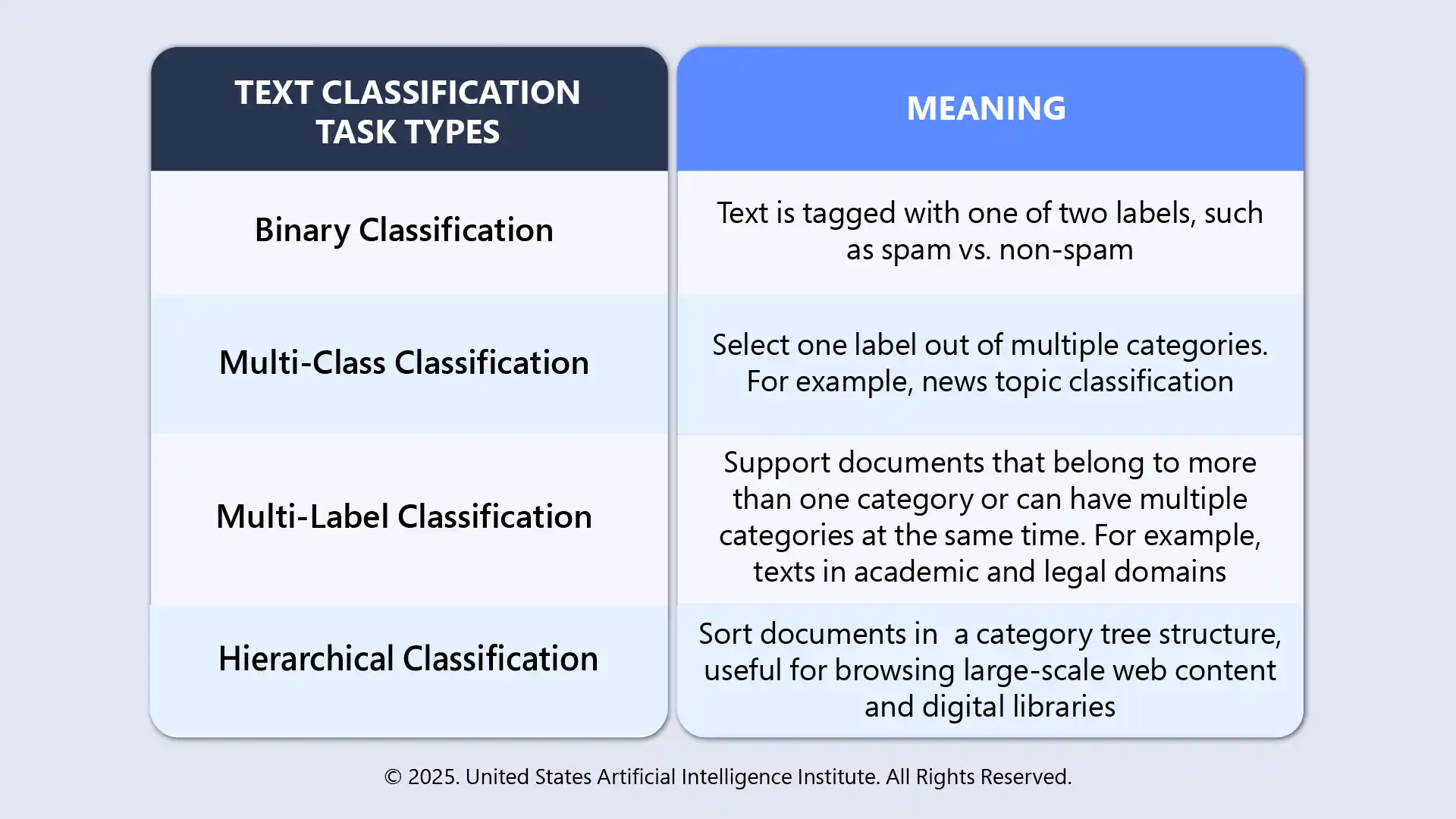
It’s critical to understand these task definitions for creating effective AI and ML skills pipelines.
How Text Classification Works?
Through the well-defined step-by-step text classification workflow, understand the role of machine and human in the process, and also get a complete understanding of how TC works:
1. Define the Objective
To put it simply, a human tells the system what to classify — for example, spam detection, sentiment analysis, or topic tagging. It is also verified in this phase if there is labeled data, which will later dictate whether supervised or unsupervised learning is employed.
2. Collect Text
Text is gathered from sources as diverse as emails, reviews, support tickets, and documents. If we've got labeled text, this supports a supervised approach; if not, the system prepares applying an unsupervised approach for pattern discovery.
3. Text Cleaning and Normalization
The model gets rid of noises, for example, punctuations, symbols, HTML tags, and redundant spaces. Text is normalized for greater uniformity across natural language processing (NLP) tasks.
4. Feature Representation
Then the text is transformed into numerical representations for model learning.
5. Model Learning
ML algorithms find patterns in data. In supervised models, examples are labeled and learned; however, unsupervised models detect similarities when no labels are provided.
6. Prediction and Evaluation
The trained model is used to classify new text, and the classifications are then evaluated (and potentially refined) before they are deployed in actual systems.
Text classification is leveraged in many industries, improving operational efficiency, and enabling intelligent decisions.
1. Document Indexing and Information Retrieval
Automated indexing provides keywords and subject headings for documents, which allows the rapid retrieval of information from large research or library systems.
2. Controlled Vocabulary and Thesauri
Classifications are made more accurate by the use of standard terminologies and hierarchical thesauri, especially for enterprise-scale databases and legal systems.
3. Automated Document Organization and Archiving
Corporations use TC to manage patents, contracts, and internal records, significantly reducing manual workload and error rates.
4. Corporate Intelligence and News Media
TC is used by organizations to forward documents to appropriate departments. Considerations, news organizations pre-classify articles in sections, e.g., politics or technology, to ensure structured publishing pipelines.
5. Content Personalization and Filtering
Personalized newsfeeds, recommendation systems, and targeted advertising use TC to connect relevant content with the preferences of users.
6. Spam Detection and Email Filtering
Spam detection, one of the most popular NLP applications, uses TC to shield users from irrelevant and harmful content.
7. Word Sense Disambiguation (WSD)
WSD clears up the ambiguity of words by utilizing the context, thus enhancing search quality, machine translations, and conversational AI systems.
8. Hierarchical Web Content Classification
Search engines and content delivery platforms weigh websites into their nested structure to allow for intuitive navigation as well as effective indexing.
If you are interested in Machine learning, check out USAII®’s latest web blog, DevOps vs MLOps vs LLMOps: Differences, Similarities, and Use Cases. Through this educational insight, you will be able to compare all the modern technical operations in 2026.
As per Gartner’s recent study, by 2027, 75% of hiring processes will include AI and ML certifications and testing for workplace AI proficiency during hiring. If you want to become a Machine Learning Engineer or an AI Engineer, explore the top AI and ML certifications, which can become a credible ladder to a successful career in the field.
Key Takeaways
As the digital world is growing faster, global data is also growing at a rapid rate, and according to Statista’s recent prediction, by 2029, the global data generation will triple. Therefore, old text classification techniques have already become outdated and too hectic to perform text classification manually.
Learning text classification provides learners with essential knowledge about how AI systems and ML algorithms work together, so they can create systems that not just read the text but also understand it and solve real-world problems instantly and accurately.
If you want to succeed in the age of AI, mastering highly useful concepts and operations such as text classification is not optional; it is essential. Start learning today and build smarter AI systems.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. Can Text Classification handle multiple languages?
Yes, text classification systems are trained well using multilingual data and ML algorithms that help them handle and work with multiple languages.
2. How do I choose between supervised and unsupervised text classification?
It totally depends on the data. If data is labeled, use supervised, and if data is not labeled, you can choose an unsupervised text classification approach.
3. How is text classification different from text clustering?
Text classification is helpful in directly assigning predefined labels to the text, whereas clustering helps in grouping similar texts without pre-assigned labels.
Follow us: