Artificial intelligence has always been software-based, with algorithms under dashboards, recommendation engines, and chatbots. In 2026, that’s rapidly changing. Robots that can see, move, and behave in their environment are bringing AI to the physical world. This change is referred to as physical AI, which entails the integration of intelligence into the physical world systems.
Humanoid robots occupy the center of this evolution, as they are designed to work within the space designed to accommodate human beings. The trend is clear: as per Precedence Research, the global market of humanoid robots is expected to be USD 2.16 billion in 2026 and will increase to USD 8.78 billion by 2035 with a CAGR of 16.91%. With this vast expansion, let’s understand how humanoid robots are gaining momentum in the next frontier of physical AI.
From Digital Intelligence to Physical Presence
Conventional AI systems are efficient in data processing, identifying patterns, and generating insights. But even the physical world is much less predictable than the digital one. The surfaces are different, the objects are not structured, and the human behavior is not consistent.
Humanoid robots fill this gap because perception, reasoning, and motion are united. They have a human-like shape, which is not aesthetic because it enables them to:
This is made possible by AI in Robotics wherein intelligence is closely linked with physical control systems.
Humanoid Robots in the Broader AI Landscape
Humanoid robots represent some of the key trends in AI, driving technological advancements in the future. They bring together autonomous agents, embodied intelligence, and responsible governance.
To comprehend their role, one can compare them to traditional automation.
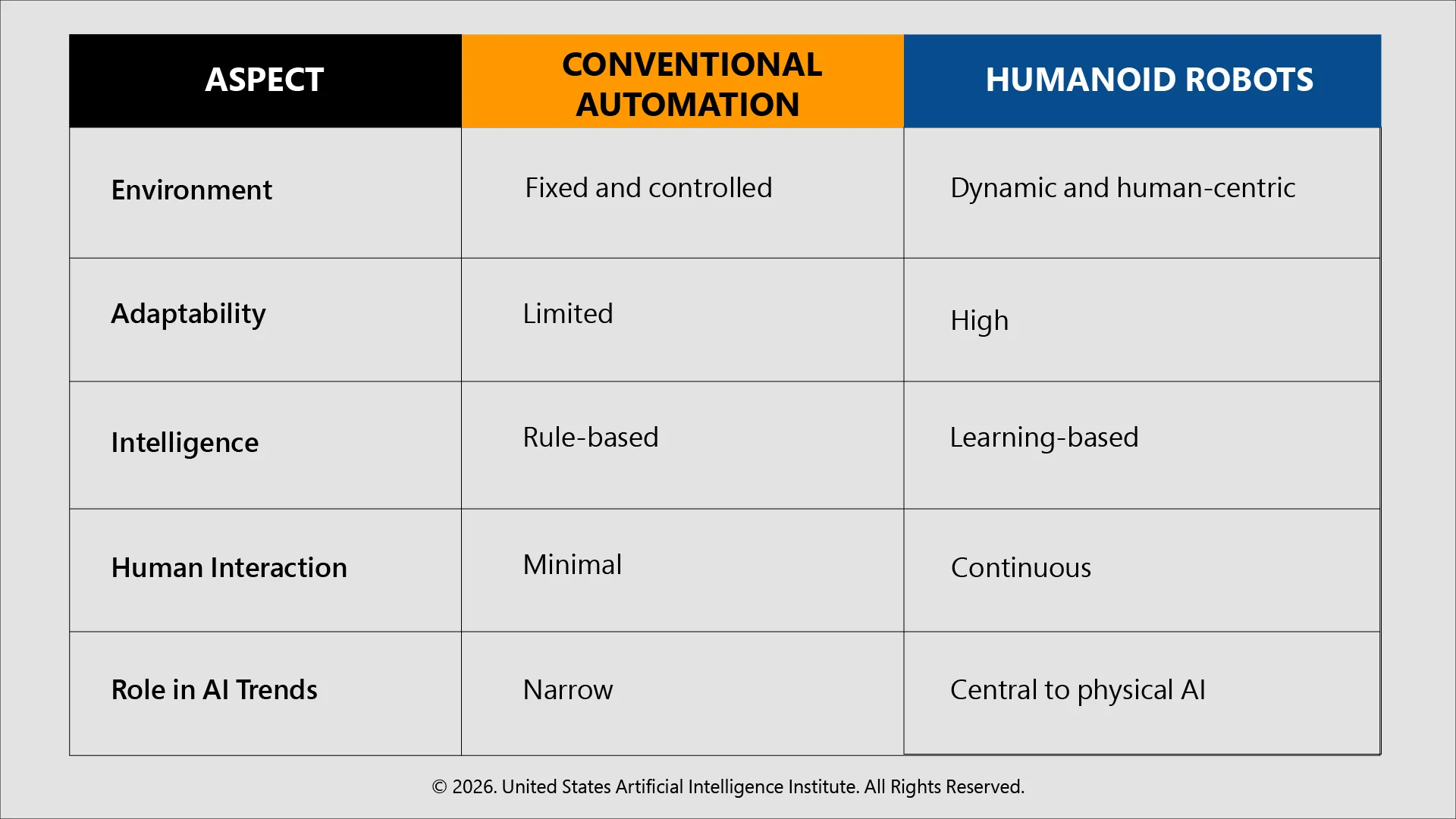
Humanoid Robots vs Conventional Automation
This comparison brings out the reasons why humanoid robots are seen as a new frontier, as opposed to a replacement of existing systems.
Why Humanoid Robots Are Gaining Momentum
The growing interest in humanoid robots is driven by practical challenges faced by organizations worldwide.
The industries are facing labor shortages, safety issues, and increased costs of operation. Traditional automation is efficient in that it can be used in a fixed environment, but fails in dynamic applications like warehouses, hospitals, etc.
Physical AI systems offer a flexible alternative. The humanoid robots can be used to help in:
With hardware getting increasingly cheaper and AI functionality growing, the stage of deployment is transitioning to the early adoption phase.
Industry Applications of Humanoid Robots
The use of humanoid robots is implemented in a variety of industries where flexibility and even human engagement are essential:
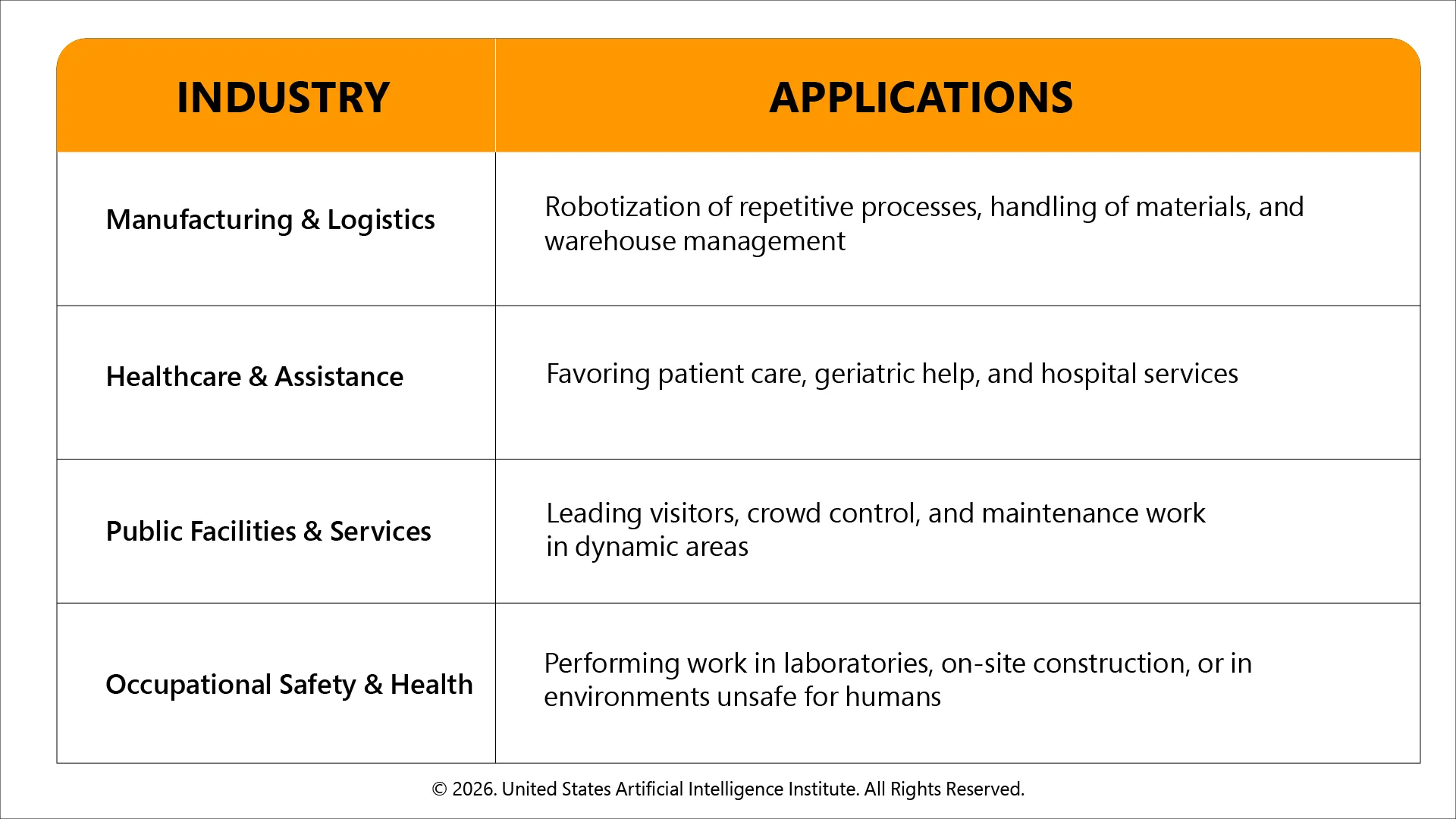
These applications underscore the fact that humanoid robots are moving beyond testing phases into real-world deployment to enhance efficiency in dynamic settings.
How Intelligence Is Built into Humanoid Robots
Contemporary humanoid robots are based on layered intelligence as opposed to having a single decision-making system. The layers have a very particular role to play, and they collaborate to facilitate autonomy.
Key components include:
This architecture is compatible with Agentic AI, which means that robots can plan their tasks, adjust to the conditions, and conduct themselves with little human control.
The Role of Learning and Algorithms
Advanced AI and ML algorithms that can be trained with the help of simulations, real-world data, and reinforcement learning are at the core of humanoid robotics.
These robots learn as they get more experience, as opposed to rule-based machines. This is a learning-based strategy that enhances flexibility and performance in the long run.
Nevertheless, difficulties also arise with the learning systems. Similar to all other AI models, robots are susceptible to AI hallucinations, where incorrect interpretation of sensory data leads to flawed actions. This necessitates safety testing and validation in the physical environment.
Challenge? Ethics and Security in Physical AI Systems
Ethical AI is an important issue as humanoid robots are in direct contact with humans. Such systems can be used in common areas, help vulnerable groups, or gather sensitive information.
Ethical design focuses on:
Simultaneously, AI security is inherent. Physical AI is based on the constant interaction of sensors and processors with control units. It can be broken and lead to failure or breach of operation.
Secure architectures are needed to make it reliable and accepted by the people.
The Evolving Role of the AI Professional
With the development of physical AI adoption, the role of AI and ML engineers is becoming larger. It has also become the expectation of engineers to develop systems that can not only be efficient but also be safe to operate with human beings.
There is a need to establish a modern training progression to narrow the digital intelligence-physical implementation divide. Top machine learning certification such as the Certified Artificial Intelligence Engineer (CAIE™) by USAII®, offer practitioners the ability to design, implement, and operate intelligent systems in practical settings.
This is a combination of skills, including AI algorithms, robotics integration, and safety measures, which is becoming very important with the transition of AI algorithms to real-life, functional applications.
Conclusion
The introduction of humanoid robots is a significant milestone in the history of artificial intelligence. They bridge the gap between cognition and physical action, enabling AI to move beyond analysis to action and interaction.
They will not be successful only because of technical progress. The collaboration between humans and intelligent machines will be determined by ethical design, high levels of security, and continuous learning.
Artificial intelligence has a new frontier that is not virtual. It is physical, adaptive, and more incorporated into day-to-day life.
FAQs
Which is the most advanced humanoid robot?
Figure 02 by Figure AI is the most advanced humanoid robot in 2026, built for human-like tasks in real environments. Boston Dynamics’ Atlas and Tesla Optimus are also top contenders.
What skills will non-technical professionals need to work alongside humanoid robots?
Basic AI literacy, understanding robot safety protocols, and the ability to collaborate with autonomous systems will be essential, even for non-engineering roles.
Will humanoid robots replace human jobs entirely?
Humanoid robots are primarily designed to augment human work, handling physically demanding or unsafe tasks rather than fully replacing workers.
Follow us: