The concept of Artificial Intelligence (AI) is changing the business, research, and development of intelligent systems. Large Language Models (LLMs) such as ChatGPT and Claude are capable of producing human-like text, but have obstacles, including outdated knowledge and AI hallucinations; the results seem believable but are not correct. To deal with these challenges, two improved models, Retrieval Augmented Generation (RAG) and Cache-Augmented Generation (CAG) augment AI by adding external knowledge or retrieved information (cached) to boost relevance, speed, and reliability.
According to Gartner, spending on generative AI will exceed 2 trillion by 2026, because organizations are keen on expanding AI beyond pilots to full-scale, real-world uses. Resulting in understanding the use of RAG vs CAG, their advantages, and real-life applications as important factors that AI professionals need to know when considering effective next-generation AI solutions.
Understanding Retrieval Augmented Generation (RAG)
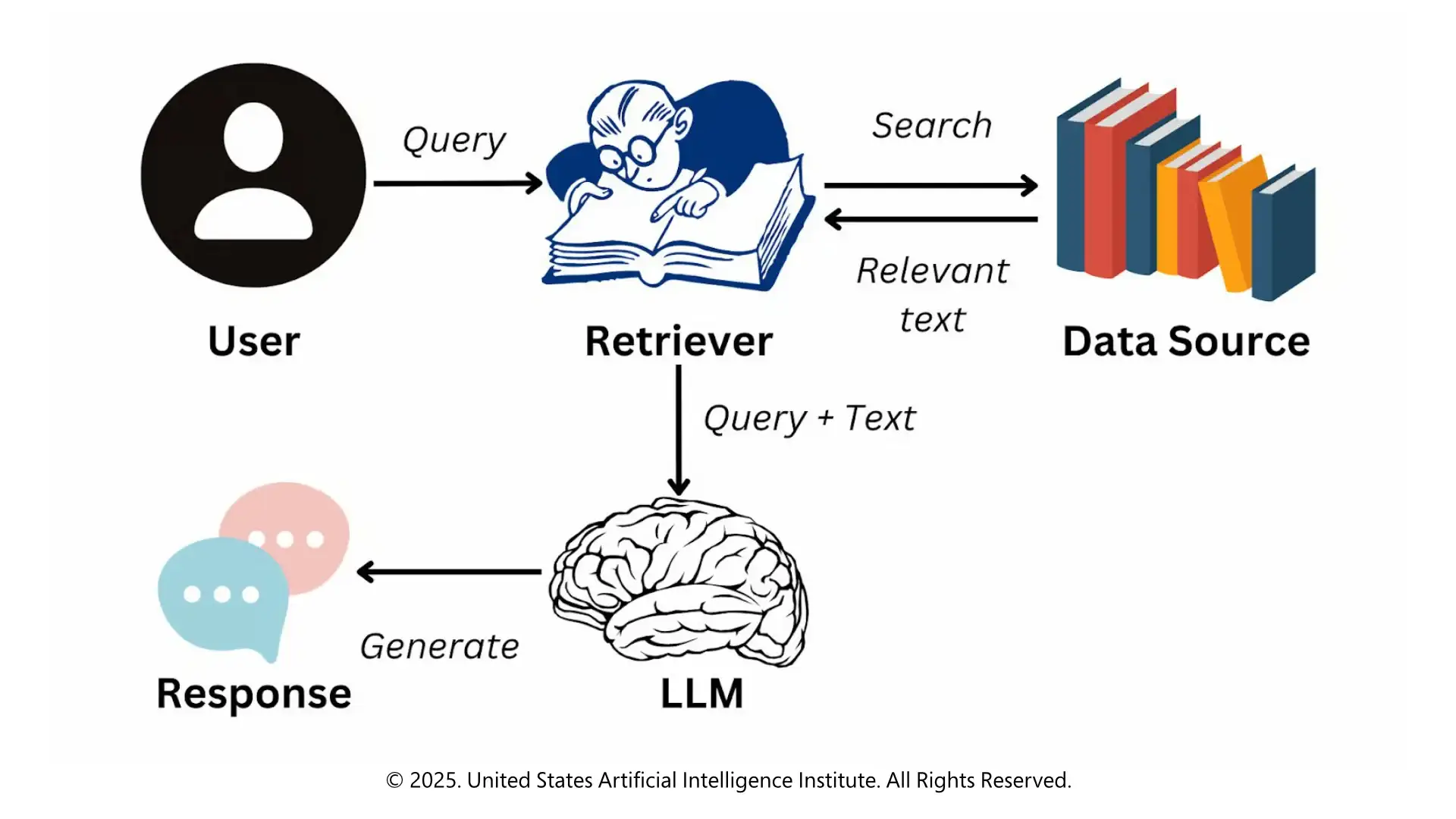
Retrieval Augmented Generation (RAG) is a type of AI method that expands the knowledge of a model after it is trained. RAG does not use only pre-trained parameters but retrieves the available information in external databases or document collections in real-time, contributing to the reduction of hallucinations and the generation of more grounded and accurate outputs.
How RAG Works
Upon a query, RAG first processes it to get the context and the intent of the query. It then does a retrieval step that attempts to find external sources with documents or data that are most relevant to the query. Lastly, the retrieved information is used together with the LLM to provide a contextual response. Such a mixture of retrieval and generation can enable RAG models to give out outputs that are informative and current.
Benefits of RAG:
Challenges of RAG
Knowledge-intensive tasks, such as AI-based customer support, legal document processing, and research assistants, are, in turn, usually carried out via RAG. It is also widely applicable in multimodal RAG systems, where text, images, and other forms of data are accessed and used to achieve more expressive AI output. Some tools, such as Langchain, allow developers to use modular pipelines to execute RAG in AI applications.
To know more about how multimodal RAG works, from text to images and beyond, you can explore this detailed guide here.
Understanding Cache-Augmented Generation (CAG)
Cache-Augmented Generation (CAG) is an AI framework that provides a way to increase fast response time and efficiency. The CAG AI can access cached information immediately without having to perform a search outside its system when it receives a query.
CAG provides advantages to applications where the user needs quick, reliable, and efficient responses, such as chatbots, FAQs, and real-time dashboards.
How CAG Works
CAG eliminates real-time retrieval using two mechanisms: knowledge caching, which preloads relevant documents into the model’s context, and key-value (KV) caching, which stores attention states. During the Q * K^T * V computation, cached keys and values are retrieved directly instead of recalculated, enabling fast, consistent responses. This best fits chat-bots, customer care, and frequently asked questions systems, where quick response is important as well as contextual memory.

Benefits of CAG
Challenges of CAG
CAG is effective in the internal enterprise systems, frequently asked questions, and knowledge bases whose data remains relatively stable, and speed is crucial. It also meshes with AI models of a real-time analytics dashboard or an automated customer service infrastructure.
Key Differences Between RAG and CAG
Although the two frameworks complement AI models, the difference between them is based on the central points of knowledge access, speed, and the focus of application:
Hybrid Solutions: Combining RAG and CAG
The most recent AI systems tend to incorporate hybrid models (RAG and CAG). An example is that commonly asked knowledge can be stored in cache memory so that it can be accessed quickly (CAG), and less popular or unpopular information is obtained on-the-fly (RAG).
It is a trade-off between latency, precision, and resource utilization, enabling AI systems to be used in a broad set of applications. Hybrid models are becoming increasingly popular in enterprise AI platforms and AI assistants as well as multimodal AI systems, where speed and data accuracy are essential.
Real-World Applications
Way Forward
To leverage CAG and RAG frameworks effectively and stay ahead in the rapidly evolving AI landscape, enroll in USAII® Top AI ML Certification, Certified Artificial Intelligence Engineer (CAIE™), which provides hands-on training in RAG, CAG, multimodal AI, and other emerging techniques, preparing learners to apply these skills confidently in practical projects and remain at the forefront of AI trends in 2026.
FAQs
Under what conditions are you supposed to fine-tune an AI model rather than use RAG or CAG?
Fine-tuning performs better in cases where domain knowledge is stable and proprietary and is used repeatedly, and does not rely on external retrieval or caching layers.
Which enhanced RAG techniques enhance the retrieval accuracy?
RAG techniques such as hybrid search, query rewriting, contextual chunking, reranking, and multi-modal RAG through frameworks such as LangChain and Haystack enhance retrieval accuracy.
What are the effects of RAG on data privacy and compliance?
To enhance compliance, RAG treats sensitive data in controlled databases, rather than retraining models, and supports regulations, such as GDPR and enterprise data governance.
Follow us: