
Classrooms continue to change at a quick pace, and at the center of this change is Artificial Intelligence. Whether it's by giving specific individualized tutoring or lending a hand in lesson planning, artificial intelligence is aiding the learning of students and providing teachers with enhanced resources for instruction.
Recent 2025 Microsoft AI in Education Report reveals educators and education leaders acknowledge the need for more AI skills training, with 54% of global educators and 76% of global leaders viewing AI literacy as an essential component of basic education for every student. In the United States, 79% of higher education educators also agree that AI literacy is essential. In this blog, we’ll explore how AI is reshaping learning today, supporting educators, and making education more accessible.
How is AI Reshaping Classrooms?
1. AI as a Tool for Students
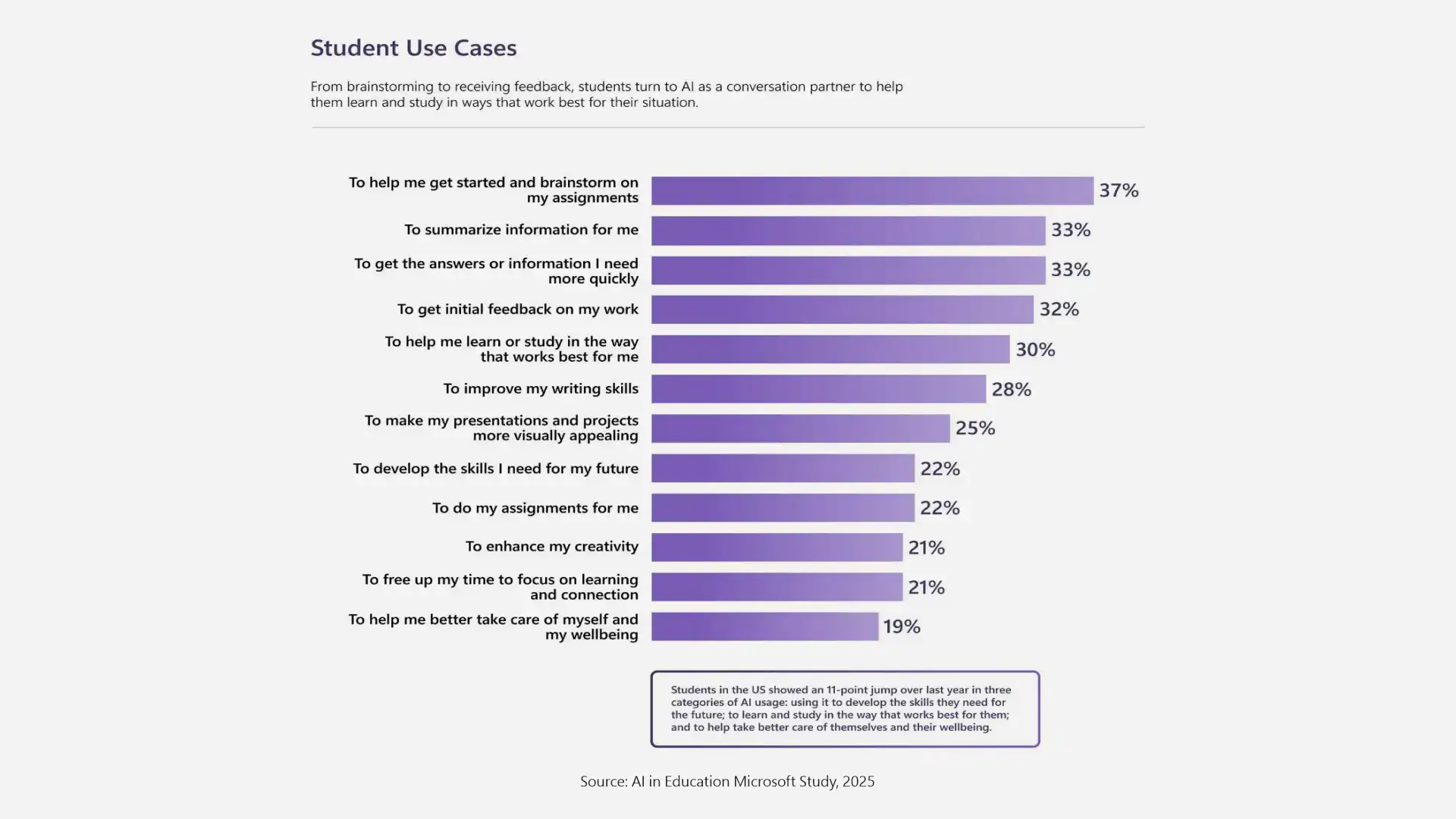
Students are starting to trust AI as a companion. While AI tutoring systems offer individualized instruction outside of the classroom, adaptive learning platforms assist in customizing lessons to each student's unique learning preferences.
Students can get help with schoolwork, concept reinforcement, and even career coaching from tools like ChatGPT, Claude, and AI companions. AI may find gaps and recommend relevant materials by examining learning patterns, increasing educational accessibility and equity for all students.
2. AI as a Tool for Teachers
Artificial intelligence in education is supporting teachers in working smarter by taking on activities such as grading, lesson planning, and tracking student learning to free up teachers to coach and mentor students.
Squirrel AI, Carnegie Learning’s MATHia, and AI chat assistants are examples of technology reinventing efficiency in the classroom. Indeed, 53% of K–12 districts with GenAI cite support to teachers as a key priority, showing the important role AI is poised to play as a classroom partner.
3. Early Adoption Patterns
The level of adoption varies by subject matter, grade level, and school type, but the trend is clear: teachers are making specific use of AI to support learning while still controlling its use in the classroom. Teachers are changing their pedagogy, using AI to enhance traditional pedagogy to increase learning.
Benefits of AI-Human Collaboration
Enhancing Teacher Efficiency
AI reduces administrative work so that educators are left with time to mentor, discuss, and create personalized guidance. This assistance also helps lessen burnout, leaving educators to focus on the human side of education, which AI cannot replicate.
Supporting Student Learning
Artificial intelligence offers opportunity for more personalized feedback and adaptive learning pathways, and teachers provide emotional intelligence and ethical guidance. Together, these capabilities allow students to receive data-informed feedback from AI, as well as wise and potentially ethical mentorship from a teacher.
Preparing Students for AI-Integrated Workplaces
Including AI in education equips students with future-ready skills for emerging jobs. Early AI literacy fosters critical thinking and problem-solving, especially in STEM. To support this growth, the United States Artificial Intelligence Institute (USAII®) offers specialized certifications:
These structured programs help students build strong AI foundations, preparing them for a workforce increasingly shaped by AI. For those looking to gain practical AI skills and certification, enrolling in USAII® AI Certifications will offer a structured path to enhance both learning and career readiness.
Challenges and the AI Skills Gap in Education
Current Challenges for Educators
In 2025, there is still a notable gap between students' awareness of AI and teachers' readiness to implement AI in classrooms. According to Forbes, while 63% of U.S. teens are using AI tools like ChatGPT for schoolwork, only 30% of teachers report feeling confident using these same AI tools. This difference emphasizes the critical need for extensive support and AI training for all educators so that they become ready and comfortable using AI in education.
Essential AI Skills for Teachers
In addition to skills in prompt engineering and bias identification, teachers need to integrate AI into their lesson plans and support students in critical thinking and responsible use of AI. Teachers must ensure that technology enhances, rather than replaces, the learning experience.
Practical Steps for Teachers and Schools
Engaging in hands-on experiences, joining AI communities, and participating in district-level training programs around AI help educators build confidence and develop expertise to implement AI into their work. Schools using an organized AI support program structure can enhance outcomes and implementation of AI.
Ethical and Academic Considerations
The emergence of AI in education necessitates striking a balance between creativity and accountability. To avoid abuse and preserve ethical norms, it is crucial to maintain academic integrity, understand AI outputs, and properly cite sources.
1. Misuse as Plagiarism or Academic Dishonesty
Generative AI's utilization in education can be seen in tools that are emerging as common usage in classrooms. Surveys by the American psychological association indicate that 7 in 10 teenagers are using AI to help them complete their homework assignments. Schools, including Ivy League institutions such as the University of Pennsylvania, promote the importance of citing AI appropriately and critically examining results for plagiarism.
Students are learning how to use external sources to validate AI results, underscoring the significance of organized AI literacy programs in assisting them in employing AI responsibly while upholding academic integrity.
2. Intellectual Property and Ethics
The emergence of AI raises issues related to copyright, data used for training, and privacy. Educational psychologists emphasize that educational AI tools must be utilized in a thoughtful manner that protects student data and intellectual property.
AI-Driven Tools and Intelligent Tutoring Systems will allow for automated lesson adaptation and assessment, relieving teachers and helping to support personalized learning experiences. With careful planning, AI will enhance human teaching and not restrict individual ethical or legal plans.
3. Promoting Equity in AI Access
4. Building a Collaborative Ecosystem
When technology and human direction are combined, AI in education flourishes. AI tools, teachers, and students work in collaboration to improve learning outcomes, engagement, and personalization.
Teacher and AI Collaboration Models
Lessons from Global Implementations
The United States, Estonia, Austria, China, South Korea, Singapore, Japan, Australia, and Canada are leading in adopting AI within education. Common strategies include redesigning assessments to reflect AI-supported skills, enhancing teachers’ ability to personalize instruction, promoting equitable access to AI tools and training, and integrating AI analytics with human mentorship to improve student outcomes.
The U.S. has strong financial backing, with Google pledging $1 billion over three years to expand AI tools and training for higher education institutions and nonprofits, reaching over 100 universities. These efforts prepare students for an AI-driven workforce while prioritizing equity, engagement, and skills.
Future Directions and Policy Considerations in AI Education
Artificial Intelligence is reshaping classrooms through adaptive, data-driven, and personalized learning. Psychologists stress studying its impact on motivation, creativity, and social-emotional growth to ensure AI enhances rather than replaces human connections. Schools are building frameworks for responsible use, equitable access, and teacher empowerment to prepare students for a human-centered, AI-supported world.
Current tools like adaptive learning and tutoring are just the beginning. By 2030, AI may act as a co-teacher and creative collaborator. These shifts raise questions on equity, critical thinking, and teacher readiness, explored further in Part 2: The Future of AI in Education, Disruptions, Dilemmas, and Directions.
Follow us: