
Artificial intelligence (AI) is changing industries worldwide, affecting areas such as health care, banking and financial services, supply chains and logistics, law enforcement, cyber security, travel, retail, e-commerce, and education. The ability of AI to analyze large datasets, automatically make decisions, and predict results provides distinct opportunities. However, with this rapid adoption, there are important moral, privacy, and governance requirements that organizations must navigate. It is not obvious to assume that perfect safe AI exists that has morality and regulatory compliance implicitly in place - it has to come as a strategic requirement.
This article examines the strategic significance of AI privacy and governance. It discusses key challenges and outlines a high-level framework that includes strategies, moral views, and case research in the evolving advanced regulatory and moral landscapes.
1. The Evolution of AI Privacy & Governance
1.1 AI Privacy and Governance
AI is required to ensure the security of user data for privacy and handle individual sensitive information responsibly. Large components include:
On the other hand, the AI regime is a broad concept that includes legal, moral, and operating structures that supervise the development, distribution, and long-lasting effects of AI. The AI regime ensures:
1.2 The Shift from Compliance to Strategic AI Governance
Traditionally, AI governance has been all about following the rules and sticking to international regulations. But these days, businesses are waking up to the fact that good AI governance can make a difference when it comes to:
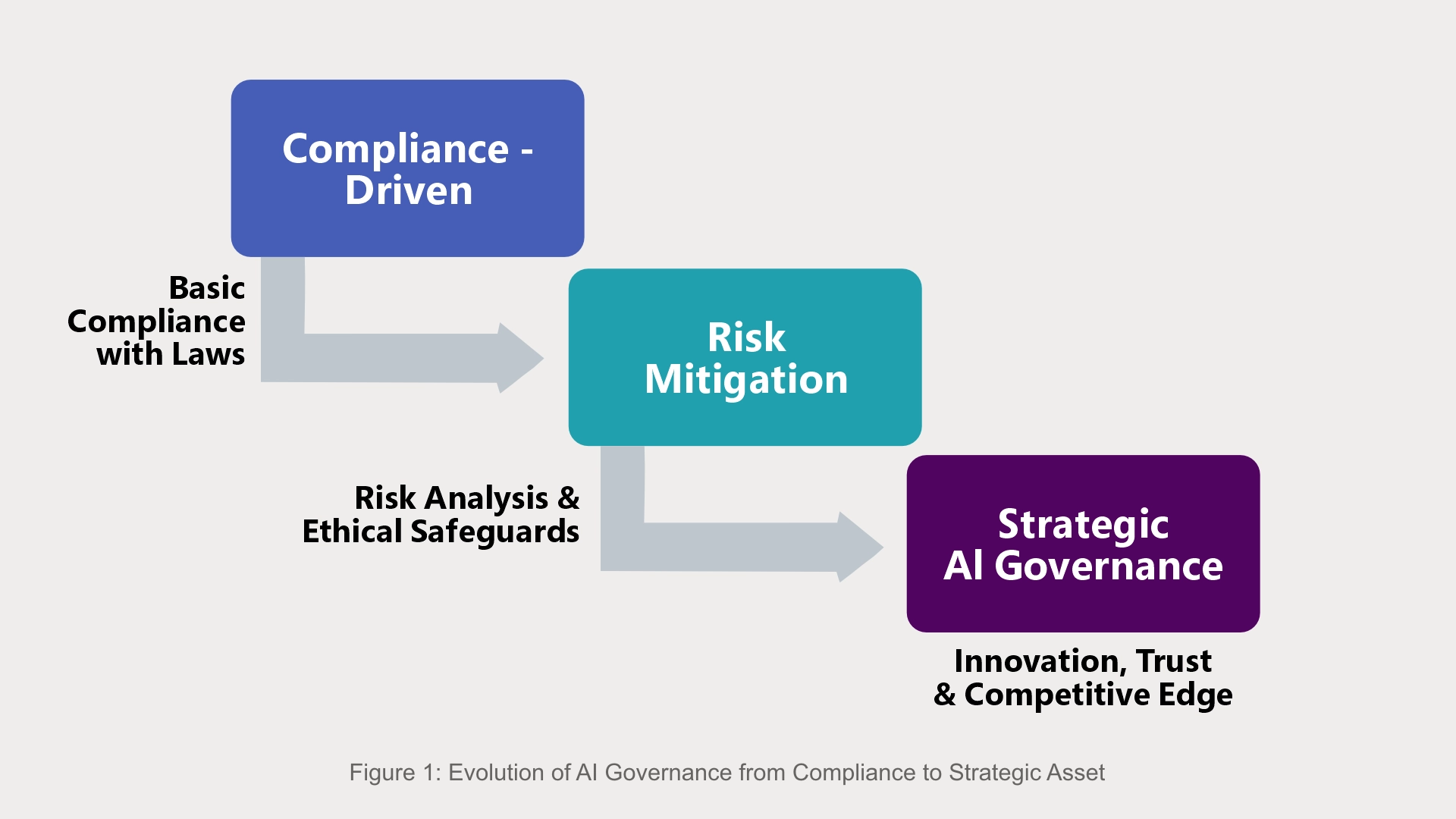
Figure 1: Evolution of AI Governance from Compliance to Strategic Asset
The AI Governance Evolution Diagram outlines three main phases in how AI governance develops:
The advancement between these phases shows how a company can move beyond simply following the rules to a more active approach to AI governance. This approach is built on trust and fits with what the business wants to achieve, what's ethically right for AI, and what the public expects.
If businesses incorporate AI privacy and governance into their business practices, they can ahead of ethical dangers. Simultaneously, they can emerge as trailblazers in innovation and show their commitment to corporate social responsibility (CSR).
2. Key Drivers of Strategic AI Privacy & Governance
2.1 Building Public Trust & Brand Reputation
More and more customers and companies are saying "no" to businesses that mishandle data or use AI in unfair ways. Being ethical with AI builds trust and keeps customers coming back. Here are a few examples:
2.2 AI Ethics as a Market Differentiator
According to a 2024 IBM study, a significant 81% of consumers show a preference for businesses that put ethical AI first. Companies adopting ethical AI guidelines see benefits like:
2.3 Encouraging Innovation While Ensuring Responsibility
Companies that embrace frameworks for responsible AI development not only reduce bias, errors, and security risk, but also promote innovation. By adhering to ethical AI principles, they can avoid:
Benefits of Strategic AI Governance
3. Comprehensive Framework for AI Privacy & Governance
3.1 Establishing AI Governance Policies
A robust framework for AI governance and regulations that ensures AI is used responsibly. The structure of this framework should encompass several important aspects:
3.2 Implementing AI Ethics Committees
Companies should form AI Ethics Committees that include people from various backgrounds as follows:
3.3 AI Risk & Compliance Monitoring
To ensure proper AI governance, it's crucial to have constant monitoring and auditing in place. Tools like IBM Watson OpenScale and Google’s What-If are implemented for ongoing AI supervision.
4. Industry-Specific AI Governance Considerations
As AI becomes increasingly frequent across diverse sectors, we must give careful attention to its management. This guarantees ethical use, adherence to guidelines, and prevention of any potential troubles. The software of AI in fields such as healthcare, finance, and law enforcement raise specific issues that need to be addressed.
4.1 AI in Healthcare
The healthcare field is increasingly more the usage of AI for things like diagnosing ailments, maintaining a watch on sufferers, and growing new drug treatments. However, incorporating AI into healthcare brings up some vital moral and privacy issues that want to be tackled with robust AI governance policies, such as:
4.2 AI in Finance
AI is gaining importance within the BFSI sectors and is leveraged appreciably in areas together with fraud detection, credit score threat assessment, or even computerized trading. However, we should continue carefully with AI's role in finance, ensuring its application is both equitable and steady. Here are a few critical concerns:
In a nutshell, AI holds colossal promise in the area of finance. We have to make certain it is used ethically, incorporates honest lending practices, adheres to the rules of Basel III and the EU AI Act, and is completely obvious in terms of fraud detection.
4.3 AI in Law Enforcement
Law Enforcement is increasingly leaning to AI for help with responsibilities like solving crimes, forecasting capacity problem spots, and tracking regions. However, we must proceed carefully with this to ensure that we are not by chance infringing on human beings’ rights. Here are some key factors we need to consider:
5. Future Trends in AI Privacy & Governance
As AI governance continues to develop, organizations need to get ready for new trends that will influence the future of responsible AI. These trends involve automating compliance, setting up AI trust scores and integrating blockchain for better accountability. These improvements will help to make sure that AI stays transparent, ethical, and in line with regulatory standards.
5.1 AI-Powered Compliance Automation
Compliance in the AI world is evolving. Instead of relying on manual efforts to follow regulations, companies are now turning to automated governance systems powered by AI. This change is crucial because rules and regulations around the globe are getting increasingly intricate and constantly changing. Businesses are now implementing several strategies, including:
5.2 AI Trust Scores for Regulatory Compliance
Governments and regulators are starting to use something called "AI Trust Score" similar to credit scores, but for artificial intelligence. AI systems will be rated based on things like security, transparency, and fairness. These scores are all about figuring out how reliable and trustworthy an AI system is. They'll do this by performing the following:
Because of this, companies will need to focus on ethically building AI and work towards getting certified through special compliance programs.
5.3 Blockchain for AI Accountability
Blockchain technology is emerging as a critical tool for AI accountability. By integrating blockchain into AI governance, organizations can:
Blockchain will play an essential role in preserving AI transparency, preventing tampering, and making sure AI decisions stay moral through the years to come.
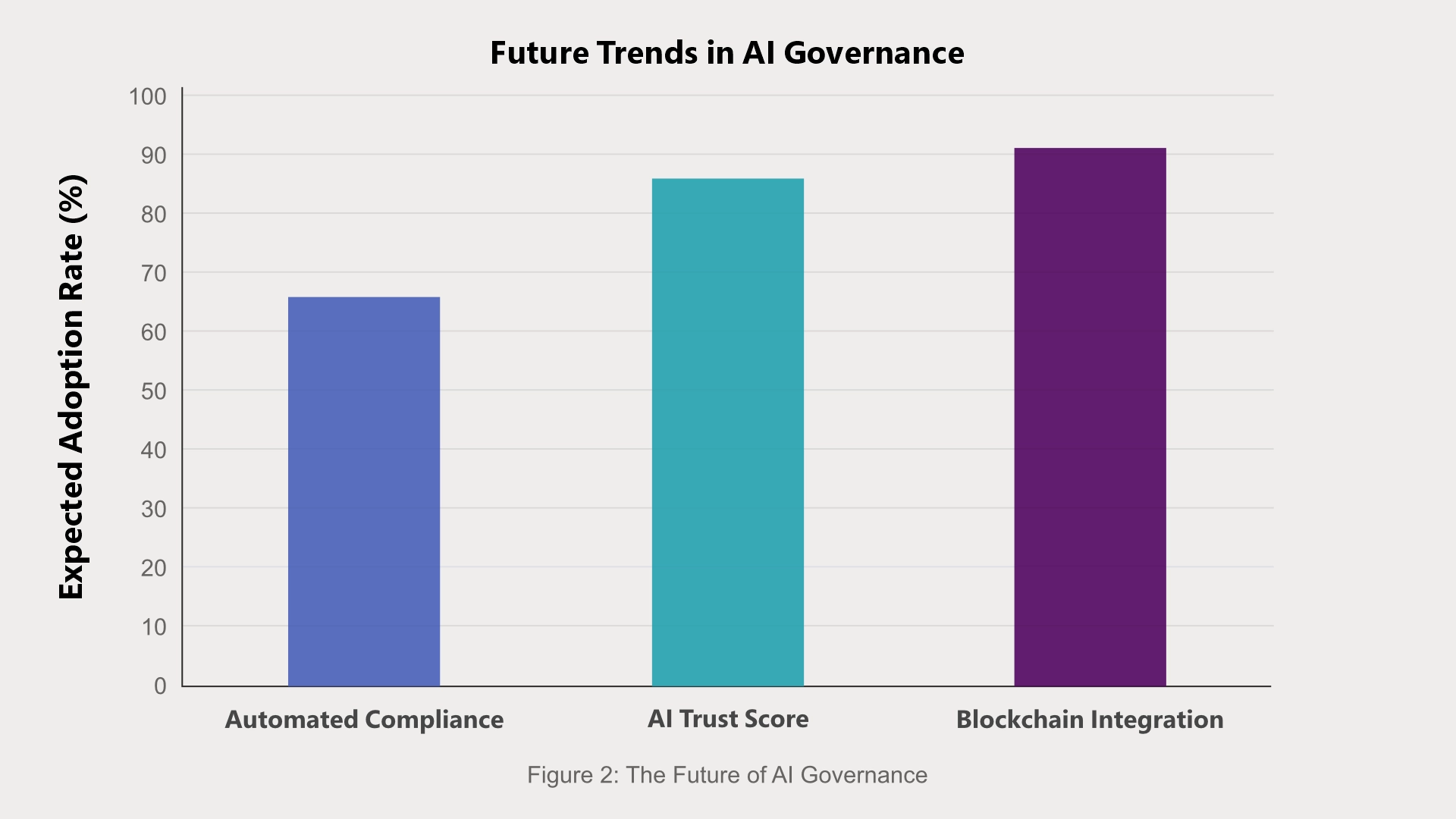
Figure 2: The Future of AI Governance
The diagram, "The Future Trends in AI Governance" uses a bar chart to show the expected adoption rates of three key AI governance trends: Automated Compliance, AI Trust Score, and Blockchain Integration.
The chart underscores the expanding importance of automation, accountability, and security in AI governance, demonstrates how these elements are shaping the future of the field.
6. Conclusion: The Future of AI Governance
Companies need to include AI privacy and good governance at the heart of their plans for AI initiatives. This requires creating AI systems that are ethical, unbiased, and follow the law are the ones who'll be leading the charge toward a more responsible AI future.
The people leading AI transformation in enterprises, must ensure that good governance isn't just about jumping through some legal hoops, but ensuring that the AI tools we use can be trusted, are morally sound, and are used responsibly. This means AI that respects people's rights, helps society grow and pushes the boundaries of innovation.
If you are leading the way for AI transformation, governance is more than just following the law. It's about making sure your AI solutions are trustworthy, ethical, and responsible. These solutions should also respect human rights, contribute to a better society, and foster new ideas and innovations.
Follow us: